As a software tester, you've probably heard many times that test coverage provides a good basis for ensuring the quality and stability of our software. But what exactly does test coverage mean, and why is it so critically important in software development and, within that, software testing?
During test coverage measurement, we not only examine how thoroughly we have tested the software code but also identify areas we have left out, which users may notice later. Thus, we can not only minimize the number of errors and bugs but also save significant money and time. If you want to learn how measuring test coverage helps improve the quality of software, this article is for you!
What does test coverage mean?
Test coverage is a popular indicator in software testing that shows how thoroughly we have tested the software code. Maximizing codebase test coverage not only minimizes errors and bugs in the code. Test coverage is crucial because it helps identify areas in the code that have not been tested yet, reducing the risk of errors during actual usage. Furthermore, proper test coverage measurement improves the efficiency of the development process since discovering and addressing errors early is simpler and more cost-effective than when problems arise later in the development process or in the live system.
To better understand the importance of test coverage, let's consider an example. Suppose a software development team is working on a new web application that offers an online shopping platform. The application has various functionalities, including browsing products, adding them to the cart, placing orders, and payment processes. As part of the development process, testers conduct tests on each functionality to examine the software's operation and discover anomalies or abnormal behaviors, known as bugs. However, if the percentage of test coverage does not reach the set goals, certain functionalities may not be adequately tested, and thus, errors may remain undiscovered. For example, if the payment functionality of the application is not thoroughly tested for all use cases, a customer may encounter problems during the payment process, such as issues with card acceptance or incorrect display of payment transactions. This can lead to significant revenue loss for both the client and the seller.
Therefore, measuring test coverage helps the product development team create reliable and stable software with minimal errors and problems, providing a better user experience for end users.
How is test coverage measured?
The first step in measuring test coverage is code instrumentation, which involves supplementing the original codebase with additional probes. The resulting augmented codebase is measurable, allowing testers to see which parts of the code were exercised during dynamic testing. Measurements can be performed at multiple levels, ranging from method-level coverage to decision, branch coverage, and even statement-level coverage. The most suitable method for a given situation is determined by the goal of testing, which necessarily includes considerations such as the domain (i.e., the type of software), the depth of testing, and business risks.
One of the most commonly used measurement levels is decision coverage, also known as branch coverage, which is supported by TestNavigator. However, it is important to consider that the more detailed picture we want to obtain of code-level coverage, the greater the performance cost may be for the application under test during runtime. It matters how many measurement points need to be inserted and how many feedbacks from probes need to be handled simultaneously.
Properly chosen coverage measurement levels and the associated testing methods can ultimately result in a much more efficient testing process.
Challenges in test coverage examination
There are several challenges to be faced during test coverage measurement. One major difficulty is selecting appropriate test cases. It is important for tests to cover all functionalities of the application but not be overly complex or time-consuming. Another challenge is the efficient management of time and resources. Achieving coverage of the entire codebase is time-consuming, and often, priority needs to be given to the most critical parts, such as higher-priority features. Regular updates and changes can pose additional challenges as tests need to adapt to these.
Simulating real environments and handling variable data can also pose challenges. Testing becomes more thorough when working with realistic data. Finally, creating appropriate reports and evaluations is crucial for understanding and optimizing the results of test coverage.
How does TestNavigator assist in test coverage examination?
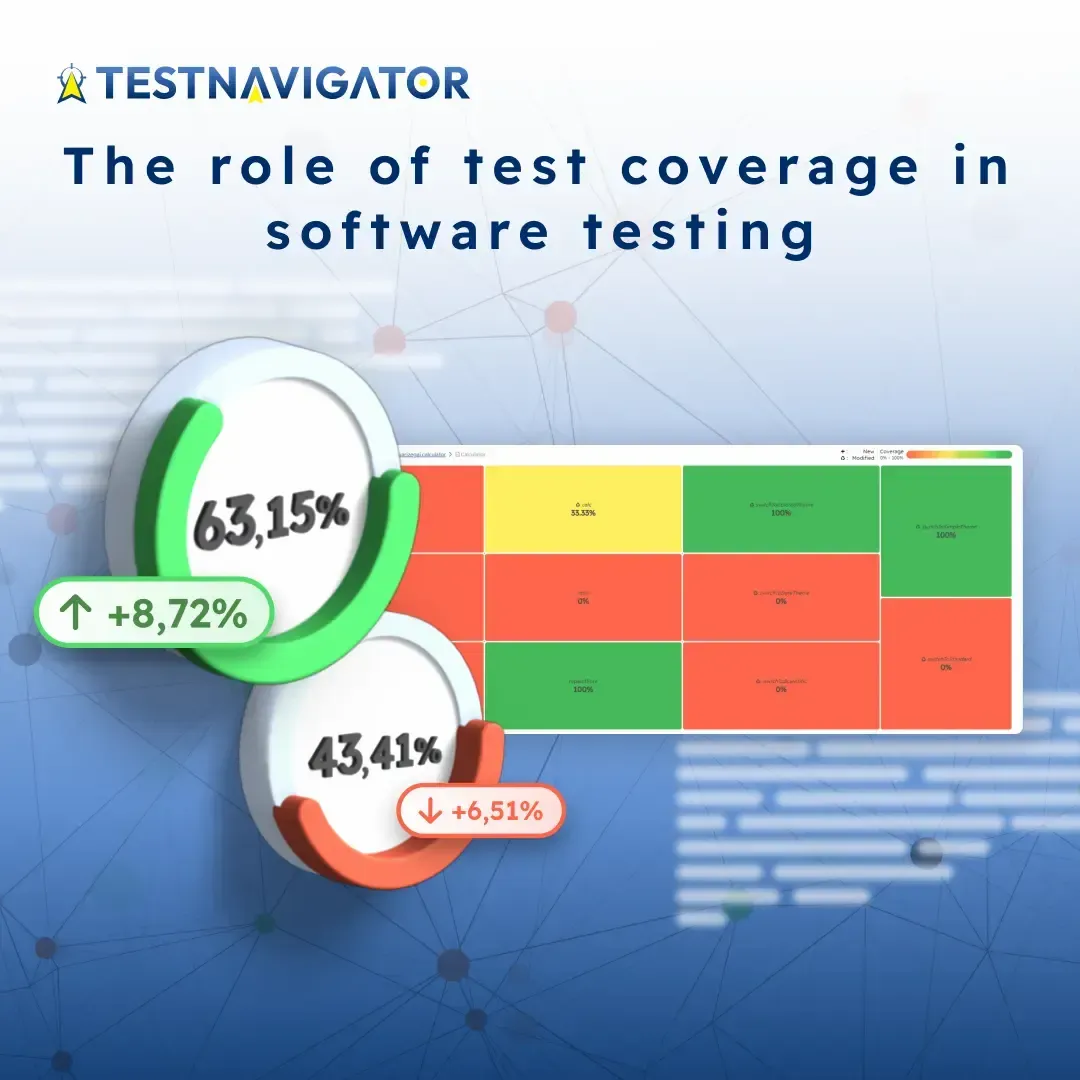
The main strength of TestNavigator lies in comprehensive test coverage measurement. It provides information in a simple and clear manner about the areas covered by tests. Through graphs and source code visualizations, missing or low coverage areas can be easily identified, allowing testers to plan more focused test coverage.
The software's ease of use is facilitated by its navigational features. Thanks to its intuitive interface, software testers can easily navigate through their test suite and immediately identify where further testing is needed. This saves time and allows for quicker responses to deficiencies or changes during software development.
TestNavigator not only provides one-time information but also delivers real-time results. Thus, testers can continuously adapt to new features and developments, ensuring continuous and comprehensive test coverage. This tool not only measures but also supports testers in creating more efficient and effective testing processes, contributing to higher-quality software releases.